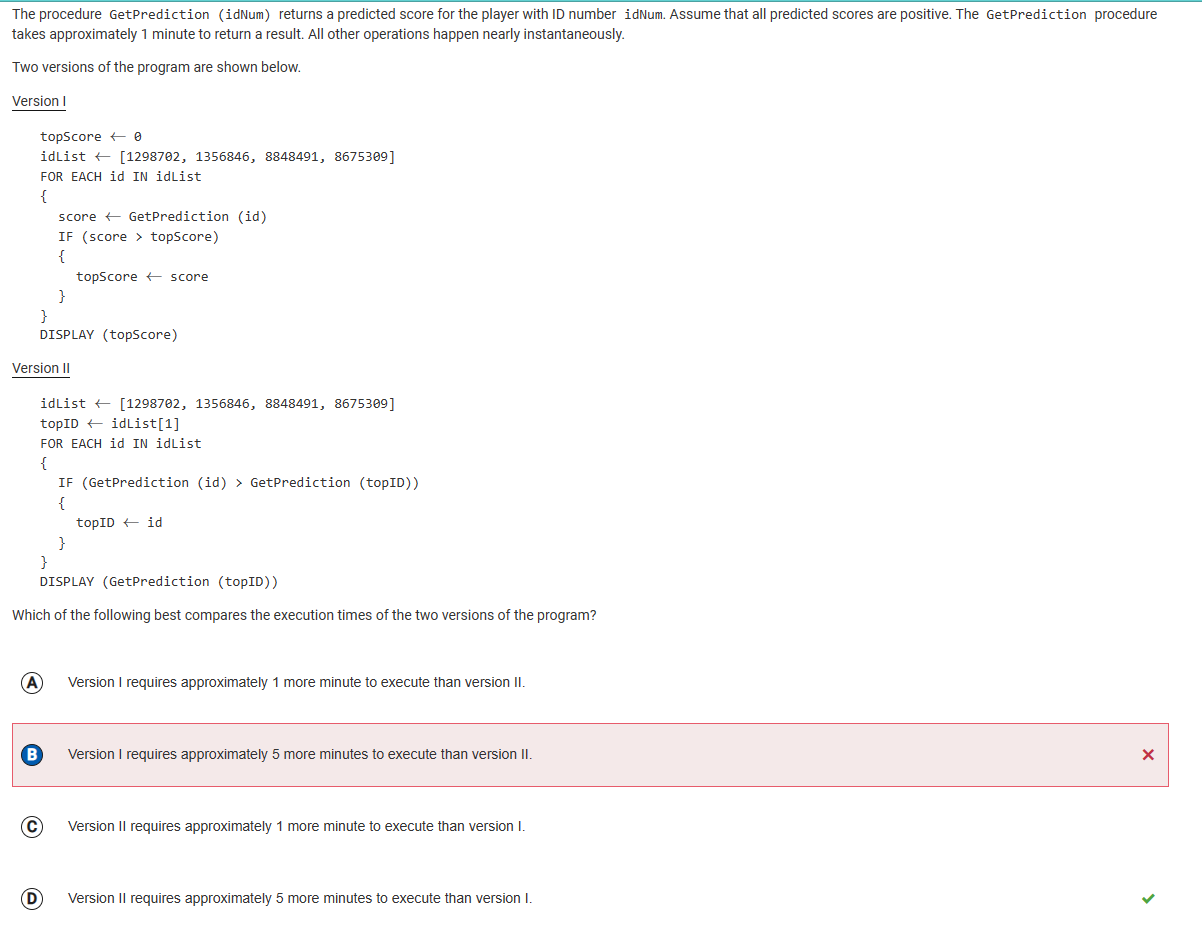
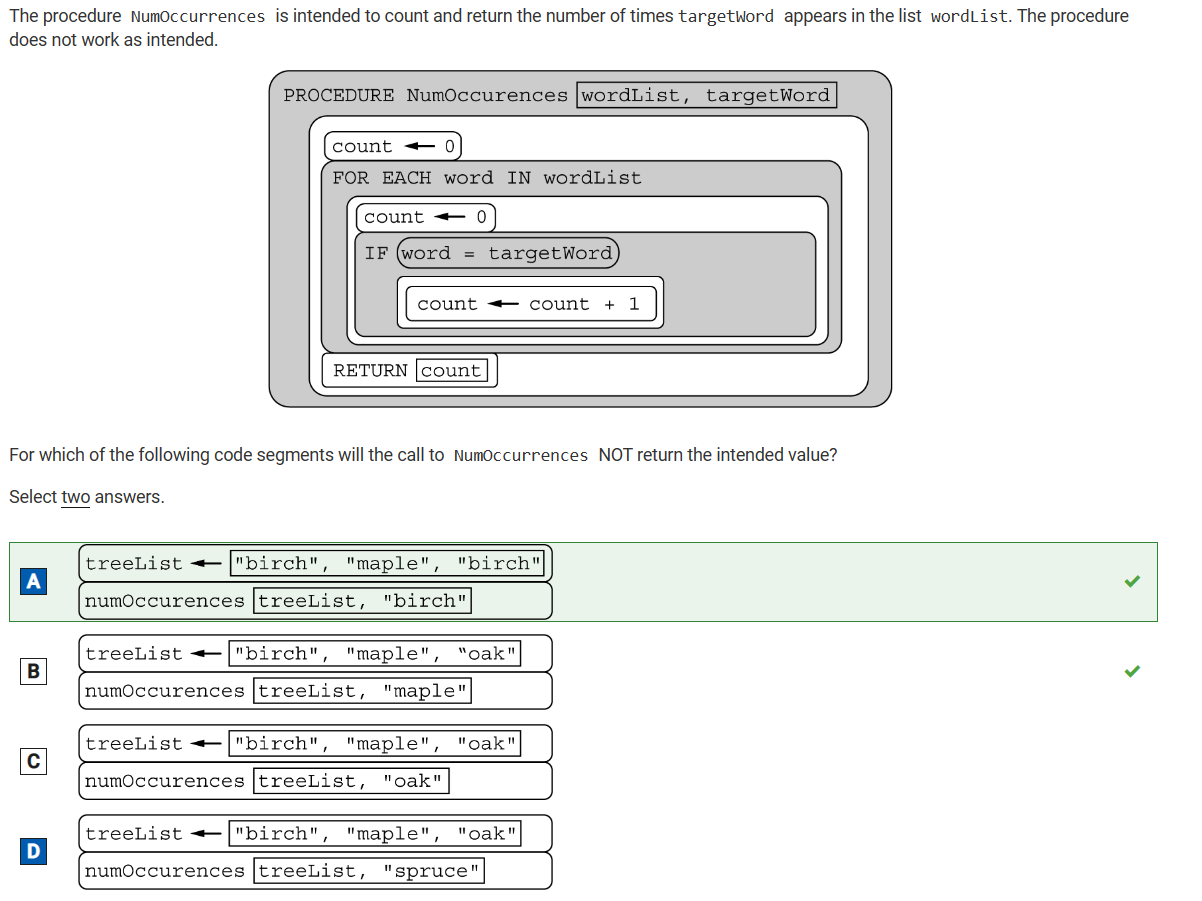
2020 Practice Test Corrections
Practice! Practice! Practice!
- Question 14: 3.3
- Question 16: 1.4
- Question 18: 3.8
- Question 26: 2.3
- Question 39: 1.4
- Question 40: 5.6
- Question 42: 3.5
- Question 50: 3.17
- Question 51: 5.5
- Question 56: 3.17
- Question 57: 4.1
- Question 59: 5.5
- Question 66: 1.4
- Question 67: 1.4
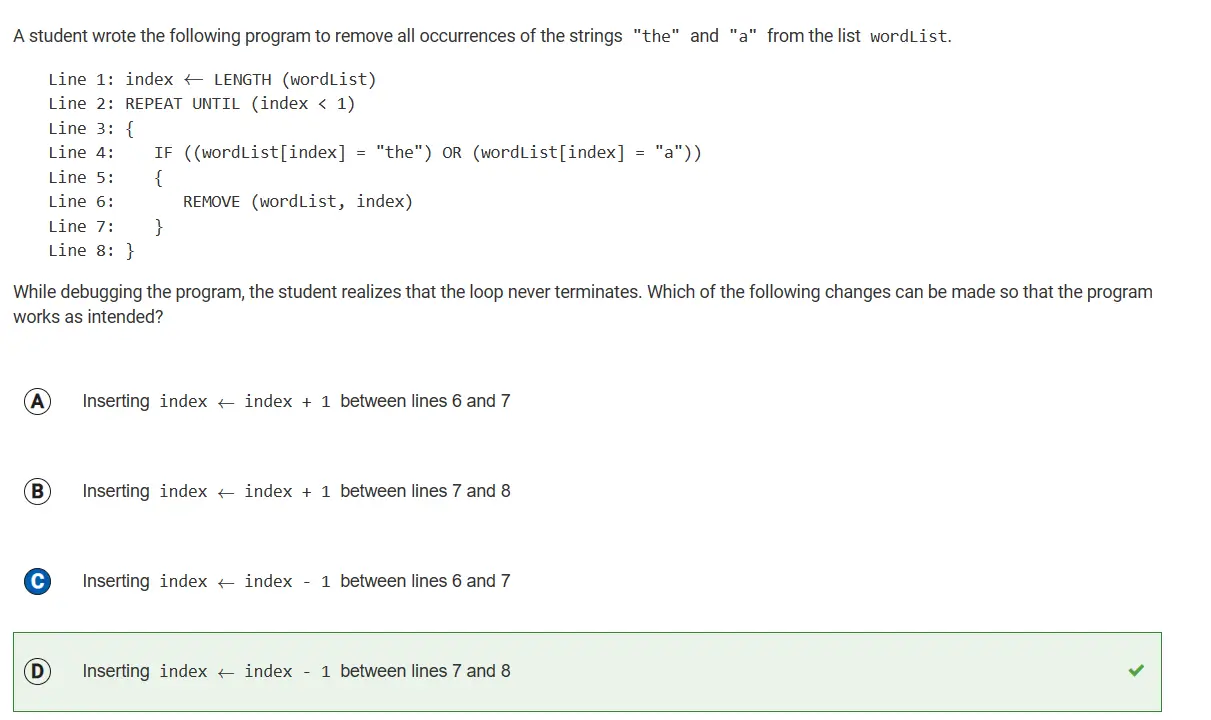
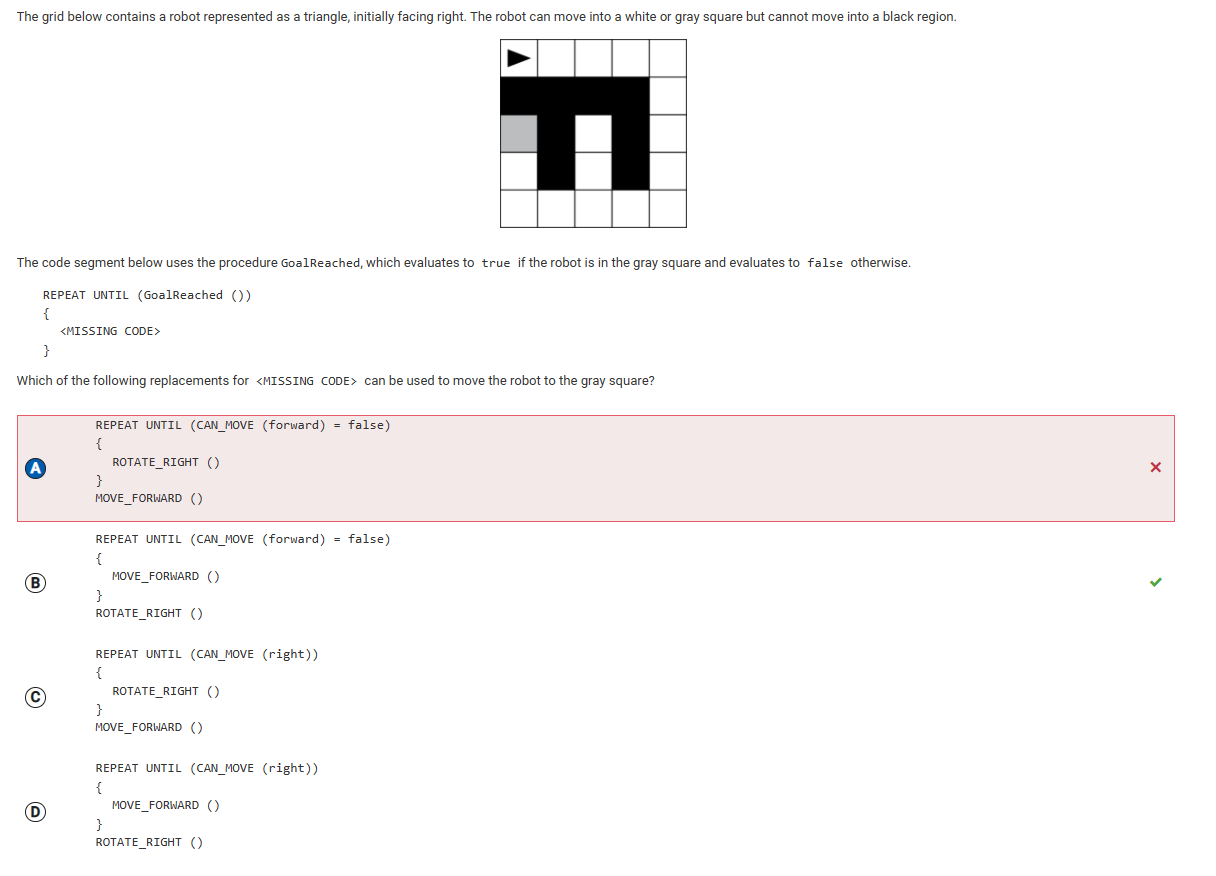
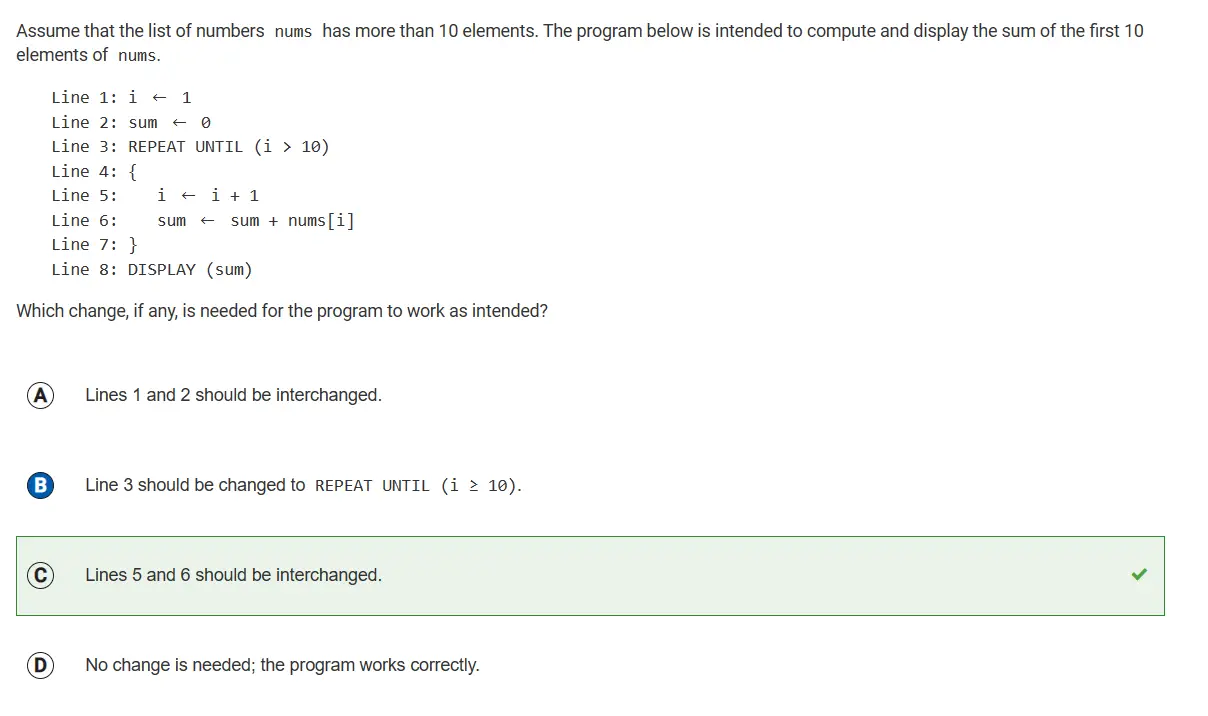
- 1.4: Identifying and Correcting Errors:
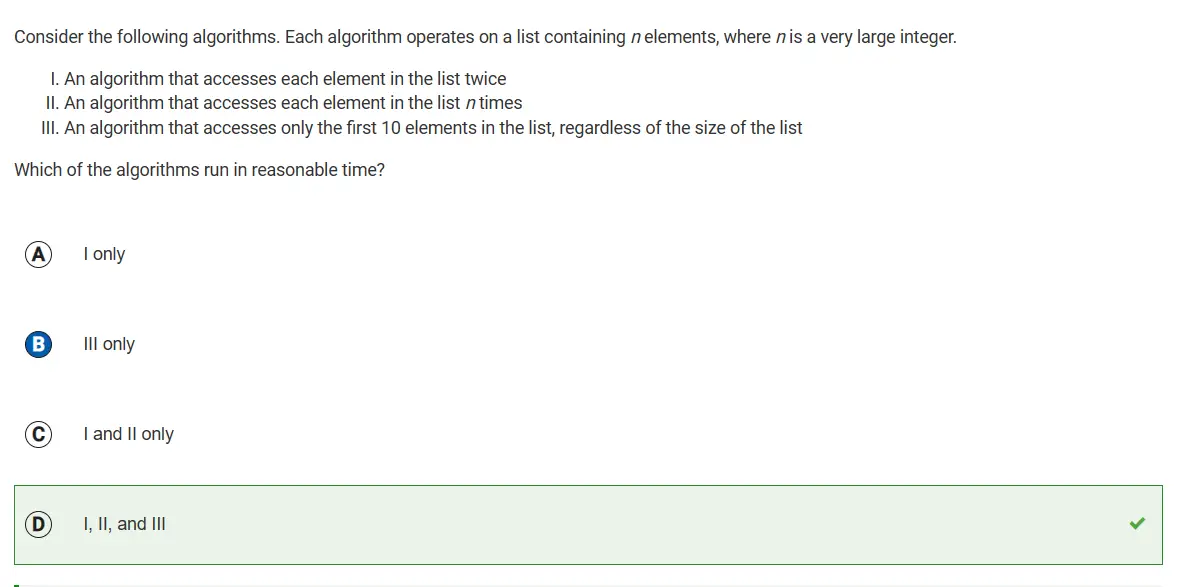
- 3.17: Algorithmic Efficiency:
- 5.5: Legal and Ethical Concerns:
I looked at the questions I got wrong and from what sections those questions are from. The sections that I kept missing the most are the ones that I looked at the college board videos of and took notes below so that I might be able to better understand the questions that I got wrong and the better prepare me for the AP exam.
1.4: Identifying and Correcting Errors:
-
Logic error is caused by the programmer making a mistake in the algorithm, which causes the program to behave unexpectedly.
-
Syntax Error is when a programmer makes a typo or writes some code/or forgets some code that doesn't follow the rules of the programming language.
-
Run-time error is when a program fails in the midst of running (in other words the program crushes) Could result from:
- dividing by zero
- inapporpriately entered a data type (such as typing a word when an integer is needed)
-
Overflow error is when a program is required to perform a calculation tht is outside of defined range of values
-
Syntax errors are usually the most easiest to correct because most integrated development environments (IDE's) display information when there is a syntax error
-
The more difficult ones to correct are logic errors
-
Hand tracing is simply writingg out the values of the variables within the loop as it iterates to determine if the outcome is correct/
3.17: Algorithmic Efficiency:
-
The steps that are in linear or sqaure steps, they run at an reasonable time but if they run at an exponential or a factorial they run at an unreasonable time
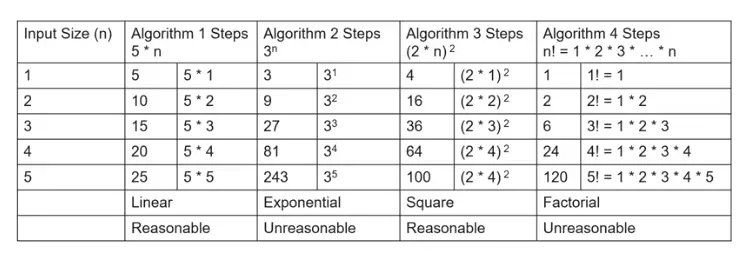
-
You can tell if an algorithm runs at an unreasonable time when the it jumps dramatically
-
a heuristic is an approach to a problem that i s not guaranteed to be optimal every time but can be used since finding the optimal solution would take an unreasonable amount of time
 This is not the best answer but then again it is not the worst
This is not the best answer but then again it is not the worst
- When deciding on whether a situation would need a heuristic solution, think about whether there is a set solution to the problem or whether there might be more than one solution and it would be difficult to determine the best solution every time.
5.5: Legal and Ethical Concerns:
-
Intelectual Property (IP): a work or invention that is the result of creativity to which one has rights
-
Copyright protects your IP and keeps anyone from using it, unless you give them your permission
-
Legal ways to use material created by someone else:
- creative commons
- open source
- open access
-
Creative Commons: provides free licenses that you can use to tell others how you want them to use your creations. It clearly tells others what they can and can noto do with your IP
-
Open source: programs made freely available for anyone to use and may be redistributed and modified.
-
Open Access: online research output free of any and all restrictions on access and free of many restrictions on use, such as copyright or license restrictions
-
Digital Divide: unequal distribution of access to technology